Critical Path Analysis Method in Primavera P6
- megaplanpm
- Mar 14, 2024
- 2 min read
Critical Path Analysis (CPA) is an invaluable tool in project management, designed to identify the sequence of dependent tasks that determine the project's completion time. This sequence, known as the "critical path," highlights tasks that, if delayed, would directly impact the project's finish date. Here's a streamlined guide to employing the Critical Path Analysis Method for project planning and execution:
Step 1: Establishing the Project Milestone
The first step in critical path analysis involves defining the project's finish date as a crucial milestone. This is often articulated as a "finish on or before" constraint, aligning with the project's contractual completion date. Setting this milestone accurately is essential, as it serves as the anchor for the entire scheduling process, ensuring that the project's timeline aligns with contractual obligations.
Step 2: Configuring Scheduling Options
After setting the project milestone, the next step is to configure your scheduling tool's settings to support critical path analysis:
- Access the scheduling option's advanced tab.
- Look for an option labeled "display multiple float paths ending with activity." This setting allows the software to identify not just the primary critical path (Float Path #1) but also secondary paths (e.g., Float Path #2), which can become critical if the primary path's tasks are completed ahead of schedule or if there are changes in project scope or resources.
For targeted analysis, such as examining a specific project package, adjust the setting to end with the final task of the package in question. This flexibility enables project managers to hone in on critical paths within specific segments of the project, ensuring focused monitoring and management.
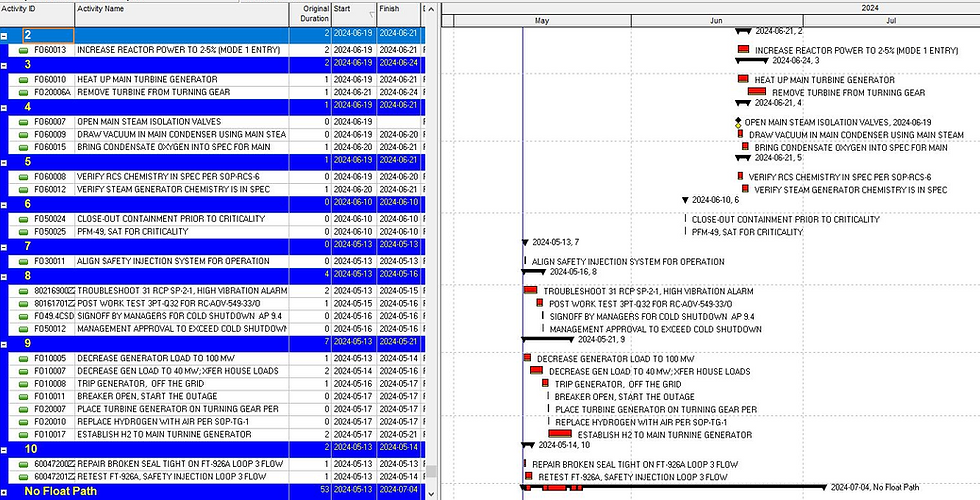
Step 3: Organizing Activities in a Gantt Chart
Once the critical paths are identified, organize the project activities in a Gantt chart based on their "float path." A Gantt chart provides a visual representation of the project schedule, where each task is displayed against time. Organizing tasks according to their float path allows project managers to easily identify and monitor the critical path, as well as secondary paths that could potentially affect the project timeline.
The concept of "float" or "slack" is crucial here. It represents the amount of time a task can be delayed without affecting the overall project timeline. The tasks on the critical path typically have zero float, meaning any delay will directly impact the project's finish date.
Key Takeaways
Critical Path Analysis is a powerful technique that enables project managers to identify the most crucial tasks that affect the project's completion time. By meticulously setting the project's finish date, configuring scheduling options to display multiple float paths, and organizing activities based on these paths, managers can ensure focused oversight and efficient resource allocation. This methodical approach not only helps in adhering to the project's contractual deadlines but also provides insights into managing task dependencies and optimizing the project schedule for successful completion.






Comments